Author: Lerato Tsebe
-
SayPro How to advance your career as an introvert.
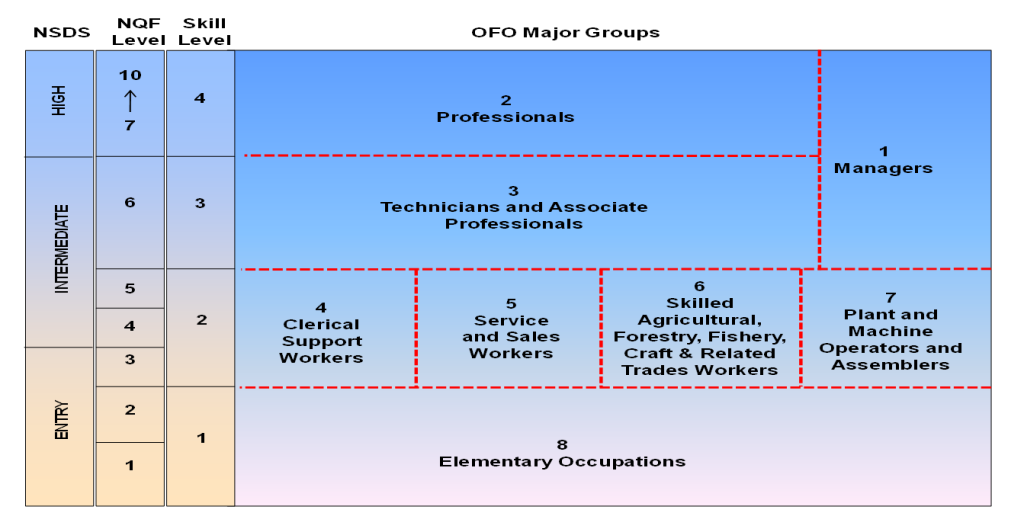
The Skill levels are defined in terms of formal education and training, previous experience and on-the-job training.
- Skill level 1
Occupations at Skill level 1 have a level of skill consisting of one of the following:
NQF Level 1 and 2 qualification;
Compulsory secondary education up to Grade 10; and
For some Occupations a short period of on-the-job training may be required in addition to or instead of the formal qualification. In some instances, no formal qualification or on-the-job training may be required
- Skill Level 2
NQF Level 3, 4 and 5 qualification or at least 1 year of relevant experience may substitute for the formal qualification; and
In some instances, relevant experience may be required in addition to the formal qualification.
- Skill Level 3
NQF Level 6 qualification
At least 3 years of relevant experience may substitute for the formal qualifications listed above.
In some instances, relevant experience and/or on-the-job-training may be required in addition to the formal qualification.
- Skill Level 4
NQF level 7 to 10 qualification; or
At least 3-5 years of relevant experience and/or on-the-job-training may be required in addition to the formal qualification.
-
SayPro How to leverage LinkedIn for career networking.
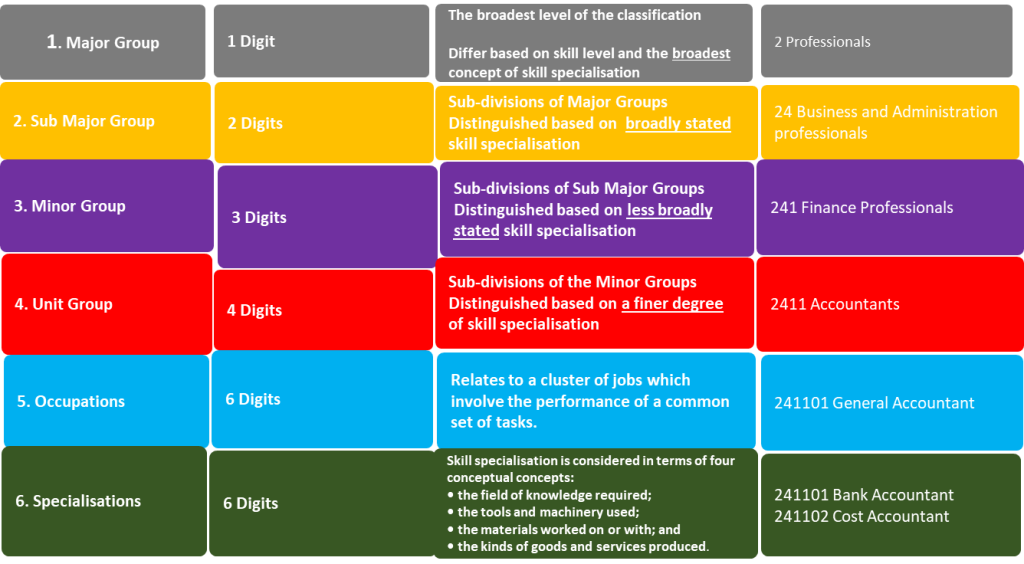
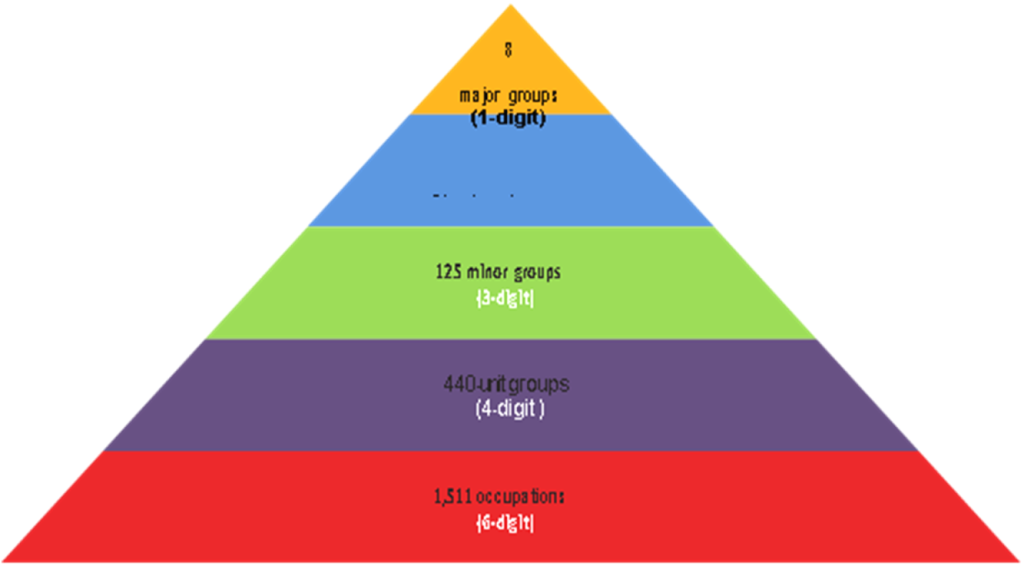
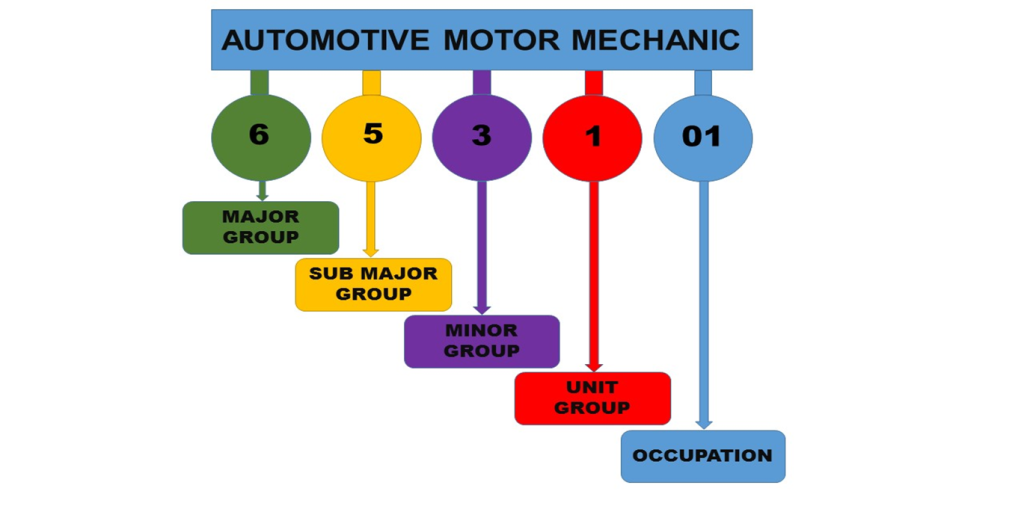
OFO codes using 2021 version (2021-653101)
-
SayPro How to prepare for career advancement opportunities.
- A job is a set of tasks and duties carried out by one person for a particular employer, including self-employment, e.g Finance Clerk
- An occupation is a set of jobs whose main tasks and duties are characterised by a high degree of similarity, e.g Finance Manager
- Specialisation can be regarded as the process of focusing an occupational concentration on a specific area of expertise, e.g Eye Surgeon.
- An occupation descriptor indicates the unique service the occupation renders or the unique product the occupation produces in executing some or all the related tasks in a specific context.
- Skill is the ability to carry out tasks and duties of a given job
-
SayPro Building a career in real estate.
- SETAs use the OFO codes to develop and report on SPOI list.
- Employers use it to plan and develop their WSPs and ATRs.
- Quality Council for Trades and Occupations (QCTO) use it as a basis for occupational qualification development and certification
- National Artisan Moderation Body (NAMB) for implementation of listed trades.
- PSET system for development of qualifications and planning for the labour market.
- Career Development Services uses the OFO for developing learning Pathways.
-
SayPro The importance of self-reflection in career planning.
- South African Standard Classification of Occupations (SASCO), Australian and New Zealand Standard of Classification of Occupations (ANZSCO) and International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO) models were considered in the development of OFO.
- In agreement with the SETAs it was decided to use ISCO as the basis for the OFO tool as it captured six digits code.
- The structure of the OFO is predetermined by ISCO standard
-
SayPro How to deal with career challenges as a minority.
- It provide information for the development of Sector Skills Plans by SETAs
- Assist with the identification of critical and scarce skills.
- Assist employers with identification and development of WSP and ATR.
- Assist SETAs to identify skills development needs, sectorial priority occupations and interventions (SPOI) in the labour market.
- Assist Post-School Education and Training (PSET) system in developing qualifications that respond to the labour market requirements
-
SayPro How to find your passion and turn it into a career.
- The OFO is a skills-based coded classification system that captures all jobs in the form of occupations and provides a framework for the identification, reporting and monitoring of skills demand and supply in the South African labour market.
- It provides a common language when talking about jobs in the form of occupations using digital codes; and
- groups occupations into successively broader categories and hierarchical levels based on similarity of tasks, skills and knowledge